LoRa
Is a wireless technology that has been developed to enable low data rate communications to be made over long distances by sensors and actuators for M2M and Internet of Things, IoT applications.
As LoRa technology is able to provide a wide area network capability, it is often referred to as LoRaWAN.
A LoRa network consists of several elements:
-
End points: The endpoints are the elements of the LoRa network where the sensing or control is undertaken. They are normally remotely located.
-
LoRa gateway : The gateway receives the communications from the LoRa endpoints and then transfers them onto the backhaul system. This part of the LoRa network can be Ethernet, cellular or any other telecommunications link wired or wireless. The gateways are connected to the network server using standard IP connections. On this way the data uses a standard protocol, but can be connected to any telecommunications network, whether public or private. In view of the similarity of a LoRa network to that of a cellular one, LoRa gateways may often be co-located with a cellular base station. In this way they are able to use spare capacity on the backhaul network.
-
Server: The LoRa network server manages the network. The network server acts to eliminate duplicate packets, schedules acknowledgement, and adapts data rates. In view of the way in which it can be deployed and connected, makes it very easy to deply a LoRa network.
-
Remote computer: a remote computer can then control the actions of the endpoints or collect data from them - the LoRa network being almost transparent.
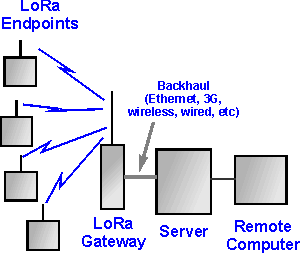
LoRa network architecture
In terms of the actual architecture for the LoRa network, the nodes are typically in a star-of-stars topology with gateways forming a transparent bridge. These relay messages between end-devices and a central network server in the backend.
Communication to end point nodes is generally bi-directional, but it is also possible to support multicast operation, and this is useful for features such as software upgrades and the like or other mass distribution messages.
LoRaWAN endpoint classes
There are many different needs to LoRa endpoints. Accordingly the LoRaWAN supports three classes of endpoints:
Class A - bi-directional end-devices: LoRaWAN class A endpoint devices provide bidirectional communications. To achieve this, each endpoint transmission is followed by two short downlink receive windows. The transmission slot scheduled by the particular endpoint is based upon the needs of the end point and also there is a small variation determined using a random time basis. LoRa Class A operation provides the lowest power option for end points that only require downlink communication from the server shortly after the end-device has sent an uplink transmission. Downlink communications from the server at any other time wait until the next scheduled uplink time.
Class B - bi-directional end-devices with scheduled receive slots: LoRa Class B devices provide the Class A functionality and in addition to this they open extra receive windows at scheduled times. To achieve the required synchronisation from the network, the endpoint receives a time synchronized Beacon from the gateway. This allows the server to know when the end-device is listening.
Class C - bi-directional end-devices with maximal receive slots: LoRa Class C devices provide nearly continuously open receive windows. They only closed when the endpoint is transmitting. This type of endpoint is suitable where large amounts of data are needed to be received rather than transmitted.
LoRa network security
The issue of network security is becoming increasingly important. As such LoRa networks require high levels of security to prevent disruption of any systems.
To achieve the required levels of security for LoRa networks, several layers of encryption have been employed:
Unique Network key (EUI64) and ensure security on network level
Unique Application key (EUI64) ensure end to end security on application level
Device specific key (EUI128)
Employing these layers of encryption ensures that the LoRa network remains sufficiently secure.
