Cisco has coined a special term — the Internet of Everything (IoE) — to further elaborate this dynamically changing phenomenon, Cisco Internet Business Solutions Group (IBSG) states that the Internet of Everything was invented in between 2008 and 2009 at the time, when “objects or things ” have more concern with Internet than people. The term IoE is somewhat similar to IoT (Internet of Things).
Imagine a world in which every device in the workplace, market, home, medical institute and/or car are connected and the world where coffee starts boiling when the morning alarm goes off, the lights automatically turn on when the car approaches the driveway, and the front door automatically unlocks when approached by a member of the household, but stays locked when a stranger arrives on the front step. This is the future and its possible with the IoE, which is based on the idea of all-round connectivity, intelligence and cognition.
So what is this Internet of Everything exactly?
The broad term known as Internet of Everything or just IoE refers to a device that is a consumer product, connected to Internet and outfitted with expanded digital features. There is a philosophy in which future of technology is composed of some different type of appliances; devices or items and these things are related to the global Internet.
Thus, Cisco defined Internet of Everything as a networked connection of different processes, people, data and things in 2013. The advantage of Internet of Everything is to connect people, data, processes, things and the values.
Cisco not only plays a vital role in the Internet of Things but also plays a leading role in network security, technologies for human interaction (in business) and industrial processes, the optimization of business and there is also a branding aspect to the Internet of Everything.
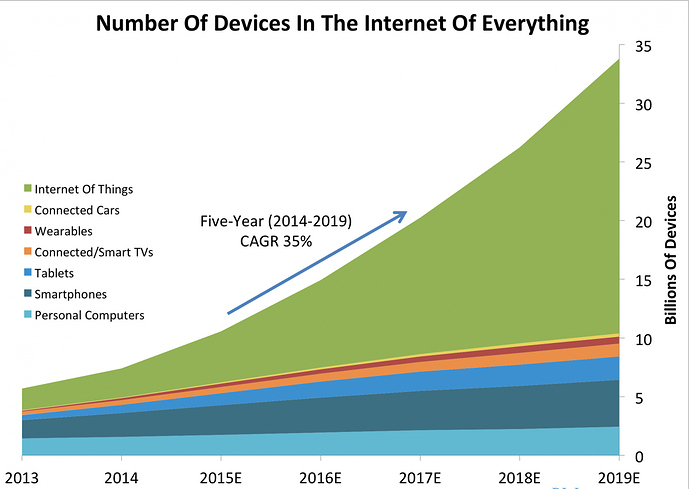
There are more things or objects than people on Earth — the tally of things that could be part of the Internet of Things vary enormously according to experts. No matter what the exact number is, it is big! For example, according to estimates made by Cisco’s Internet Business Solutions Group, some 25 billion devices were already connected to the Internet in 2015, and this number may grow to 50 billion by 2020. These things include mobile devices, parking meters, thermostats, cardiac monitors, tyres, roads, cars, supermarket shelves and even cattle.
Ericsson also predicts that fifty billion (50B) devices will be connected to the Internet by 2020, dwarfing the scale and scope of the Internet and mobile world, as we know them today. A study conducted by Cisco on the ”Internet of Everything” claims that IoE will have a market potential of USD 14.4 trillion by 2022.
Pillars of Internet of Everything (IoE)
People : Connecting people in more relevant, valuable ways.
Data: Converting data into intelligence to make better decisions.
Process: Delivering the right information to the right person (or machine) at the right time.
Things : Physical devices and objects connected to the Internet and each other for intelligent decision-making; often called Internet of Things (IoT).
Internet of Everything vs. Internet of Things
Internet of Things (IoT) and Internet of Everything (IoE) are two different concepts and a main difference between them is the number of pillars:
-
Internet of Things (IoT) focuses on physical objects only. Whereas,
-
Internet of Everything (IoE) encompasses four components (things, processes, data and people).
The IoT, in essence, is the interconnectivity of physical objects that send and receive data, while IoE on the other hand is a wider term that (apart from IoT) includes, numerous technologies and people as the end-nodes. For detailed report on the differences, please follow IoT vs IoE.
Similarities between IoT AND IoE
Internet of Thing (IoT) and Internet of Everything (IoE) are two different terms but there are some similarities between them as described below:
Decentralization
Both Internet of Thing (IoT) and Internet of Everything (IoE) don’t have any single center rather they are distributed systems, each node work as a small management center and is able to perform different tasks independently.
Security Problem
Distributed systems are still highly vulnerable to cyber attacks; the more devices are connected to the network, the higher the susceptibility the breaches.
On one hand, decentralization is one of the advantages for both IoT and IoE, since the whole system doesn’t fail even if there are problems in a couple of nodes. On the other hand, such a distribution causes disadvantages in the form of threats for data security and personal privacy.
For Example
Every industry can apply the Internet of Everything model into its processes to get benefit from it. Here are some general examples:
Municipality systems can implement smart water and electricity meters for residents and commercial organizations in order to monitor usage rates and make decisions concerning economy and cutting costs.
The manufacturing industry can implement sensors for predictive maintenance into production to monitor equipment parts that need to be fixed or replaced. This helps to eliminate downtime and reduce the fixing costs.
Logistics and delivery companies can introduce sensors and smart devices on trucks to optimize delivery conditions and possible routing. Eventually, companies can improve end-user satisfaction.
While the term IoT is mainly used for devices that wouldn’t usually be generally expected to have an Internet connection, and that can communicate with the network independently of human action. That’s why, a smartphone isn’t generally considered an IoT device and neither is a PC, even though the latter is crammed with sensors. However, a smartwatch or a fitness band or other wearable device might be counted as an IoT device.
Role of IoE in the field of DEFENCE
The Internet of Everything or IoE, is facilitating as a catalyst to change the landscape of the technological world, while transforming how users leverage network-based solutions. In defence, IoE plays a vital role, and holds the power to connect the battlefield with the digital world.
Today’s military is acquiring to asymmetrical warfare and an evolving real-time threat matrix that requires new approach to military operations.
In this era of technology, from the fixed-location work models of the PC era to the mobile, social, virtual and today’s collaborative model, information advantage has become most important than overwhelming force. To fulfill those needs, our military is taking a leap forward by obtaining new technologies and incorporating them into existing environments, and without sacrificing security and the ability to manage complex systems.
The evolution of military technology also allows unification of computing, storage and networks with sensors, devices and collaborative applications. An integrated architecture for IoE creates collaboration of physical and virtual environments that connect IoT devices with secure virtualization, mobility, unified communications and other advanced technologies.
ADVANTAGES of Internet of Everything (IoE)
IoE promises to take IoT to the next level by combining people, processes and technology with connected devices, sensors and other machines. This collaboration of IoT with human communication and analytical elements enable real-time decision advantages.
The opportunity with IoE comes from its ability to interlink the components via an intelligent, programmable network. IoE is a sensitive part of this evolution, in which physical objects like vehicles, weapons are connected to secure networks to create information dominance.
DOD’s (Department of Defence) vision of net-centric includes four key elements; (1) with improved information sharing; sharing information, (2) collaboration that increases the quality and awareness; shared awareness, (3) that enables self-synchronization, (4) and lastly the integration of the other three elements to increase effectiveness of mission.
IoT was the innovation of 1990s, which is now a reality. IoE is building the industry, both from a technology standpoint and within the enterprise. It is not just creating more innovative technologies, but it is also creating a fully new field of jobs that have never been seen before.